Today, we present a guest post written by Jeffrey Frankel, Harpel Professor at Harvard’s Kennedy School of Government, and formerly a member of the White House Council of Economic Advisers. A shorter version appeared in Project Syndicate.
Category Archives: exchange rates
Manufacturing Employment and Output
Today’s employment situation release depicted a picture of continuing recovery in the labor market. One interesting aspect is what is happening to the tradables sector, which I proxy with the manufacturing sector. There, the advance data indicate a slight decline.
As the CNY Goes, East Asia Goes…Maybe
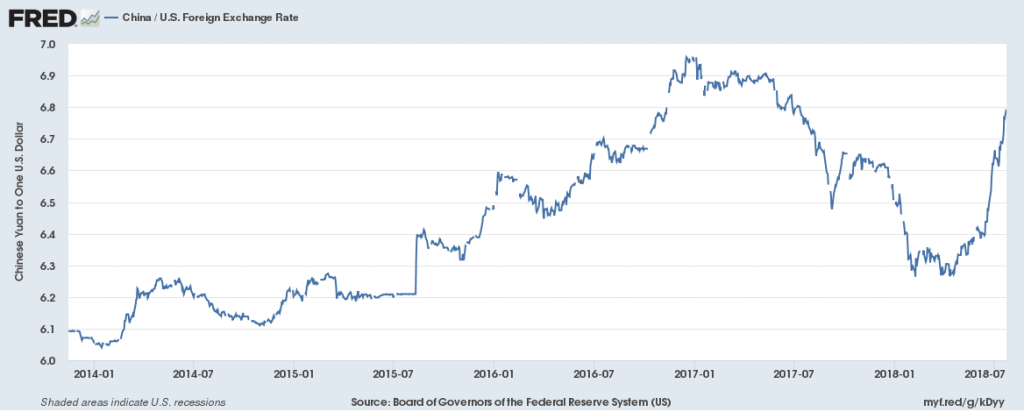
For whatever reasons — capital outflows, PBoC non-intervention — the yuan has depreciated substantially since the Trump administration has announced Section 301 actions against China. This has implications not just for the CNY/USD exchange rate, but also other East Asian currencies.
At Business Cycle Frequencies, Macro Dominates in Trade Flows
VoxEU: “The new Fama Puzzle”
That’s a new article at the outstanding web portal VoxEU, coauthored by Matthieu Bussière, Menzie Chinn, Laurent Ferrara, and Jonas Heipertz, and based on this paper:
The ‘Fama puzzle’ is the finding that ex post depreciation and interest differentials are negatively correlated, contrary to what theory suggests. This column re-examines the puzzle for eight advanced country exchange rates against the US dollar, over the period up to February 2016. The rejection of the joint hypothesis of uncovered interest parity and rational expectations still occurs, but with much less frequency. In contrast to earlier findings, the Fama regression coefficient is positive and large in the period after the Global Crisis, but survey-based measures of exchange rate expectations reveal greater evidence in favour of uncovered interest parity.
Explaining the Soybean Selloff: Ag Conditions, the Dollar, or Tariff Fears?
Trade Deficit Rising!
Since 2017Q1. By Mr. Trump’s own metric, we’re losing. But it’s a stoopid metric for evaluating “unfair”-ness.
Long Horizon Uncovered Interest Parity, Updated
About twenty years ago, while visiting the Research Department of the IMF, Guy Meredith poked his head in my office and wondered aloud whether interest differentials could reliably predict (in the right direction) subsequent exchange rate changes at horizons of three to five years. The resulting paper led in turn to production of this graph:
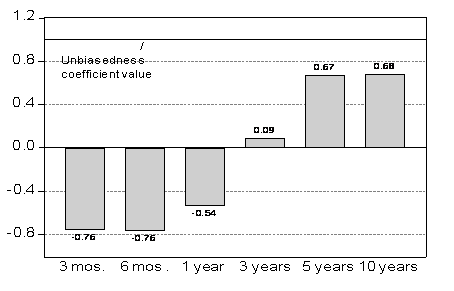
Figure 1: Panel beta coefficients at different horizons. Notes: up to 12 months, panel estimates for 6 currencies against US$, euro deposit rates, 1980Q1-2000Q4; 3-year results are zero-coupon yields, 1976Q1-1999Q2; 5 and 10 years, constant yields to maturity, 1980Q1-2000Q4 and 1983Q1-2000Q4 (last observation corresponds to exchange rate data). Source: Chinn (2006).
Guest Contribution: “Exchange rate forecasting on a napkin”
Today we are fortunate to present a guest post written by Michele Ca’ Zorzi (ECB) and Michal Rubaszek (SGH Warsaw School of Economics). The views expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the ECB.
We have just released a new ECB Working Paper entitled “Exchange rate forecasting on a napkin”. The title highlights our desire to go back to basics on the topic of exchange rate forecasting, after a work-intensive attempt to beat the random walk (RW) with sophisticated structural models (“Exchange rate forecasting with DSGE models,”).
Guest Contribution: “The ECB’s Strong Euro Problem”
Today, we are fortunate to present a guest contribution written by Ashoka Mody, Charles and Marie Visiting Professor in International Economic Policy, Woodrow Wilson School, Princeton University. Previously, he was Deputy Director in the International Monetary Fund’s Research and European Departments.
The euro has appreciated 10 percent against the Swiss franc (CHF) over the past year. The U.S. dollar and the Japanese yen have not made similar gains vis-à-vis the franc. Tracking the franc’s movements relative to the major currencies gives an unusual window onto the deflation-fighting credentials of the world’s major central banks. It illustrates, in particular, the European Central Bank’s half-hearted efforts to fight the risk of price deflation. Financial markets have come to believe that the ECB will prematurely tighten monetary policy: hence, despite brief episodes of depreciation, the euro will tend to stay strong, hurting economic prospects in several eurozone member countries.