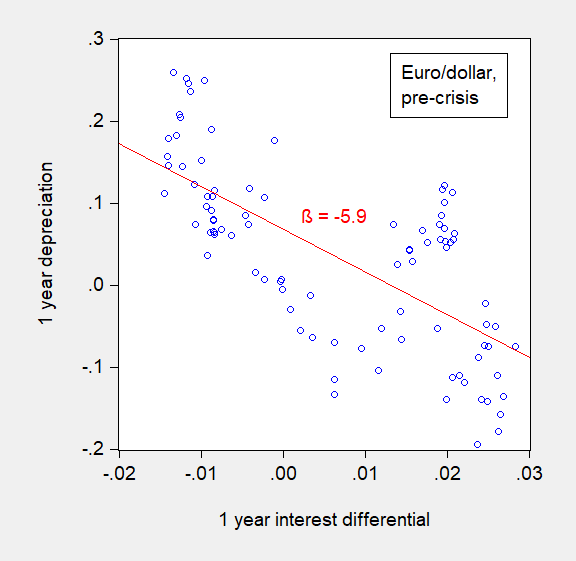
There was no recession after Brexit. But a slowdown looks like it’s here now…
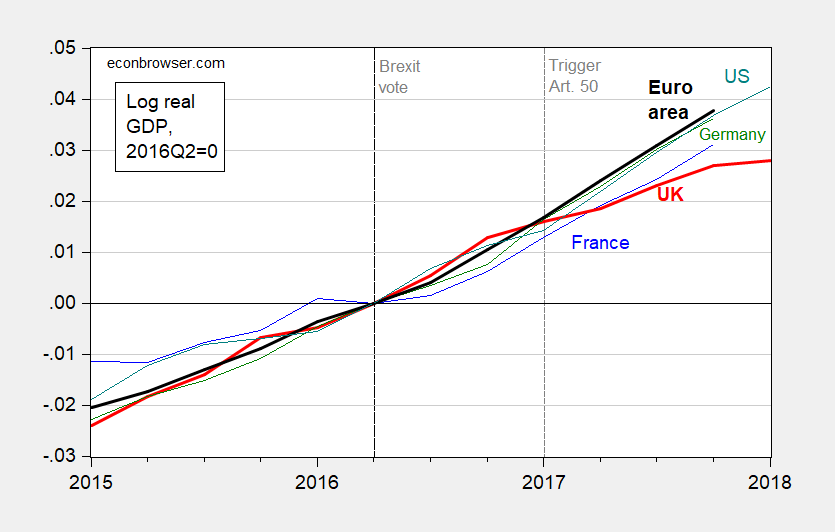
Figure 1: Log real GDP for France (blue), UK (bold red), Germany (green), US (bold blackteal), and euro area (tealbold black), all normalized to 2016Q2. Source: OECD, BEA, author’s calculations.
Continue reading