Today we are pleased to present a guest contribution written by Christopher A. Hartwell (ZHAW School of Management and Law, Switzerland), and Pierre Siklos (Professor Emeritus at Wilfrid Laurier University; and Balsillie School of International Affairs, Canada).
A paper by the two of us, forthcoming in the International Journal of Central Banking, makes the case that poorly performing central banks – in particular, ones that continually miss their inflationary targets – not only undermine their own credibility, but also undermine a country’s institutional quality. Therefore, when asking: What Damage Can a Poorly Performing Central Bank Do? The answer is: quite a lot, actually. Such a conclusion has far-reaching ramifications for institutional development, leading to less overall economic resilience.
Ever since the policy of central bank autonomy spread around the globe, monetary authorities have played, some would say, an outsized role in determining the path of a country’s economy. Given this importance, we hypothesize that how a central bank performs can have a substantial influence on not only the performance of the economy but the strength of its institutions. For example, short-term declines in central bank credibility, a flow variable, imply a parallel decline in the overall trust placed in central banks, with trust a slower-moving stock-like variable. If this trust begins to ebb away from the central bank, there is the potential to degrade a country’s institutions more broadly. Weaker institutions translate into less institutional resilience in an economy. We think of resilience as the ability of a country to withstand shocks, potentially of both the economic and political variety.
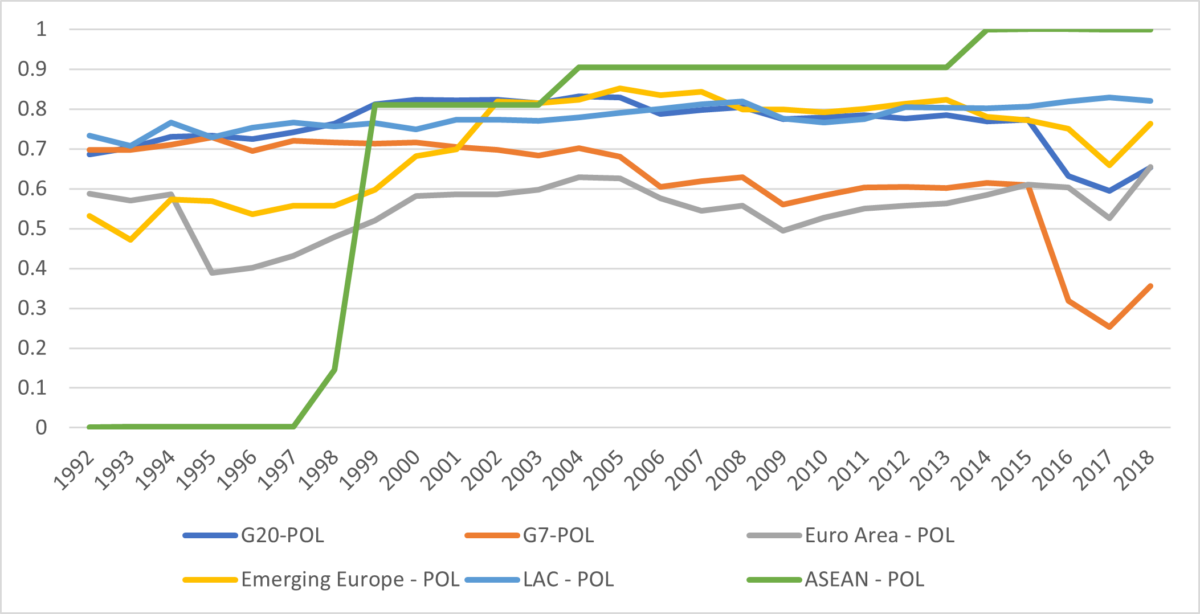
To quantify this relationship, we construct an index of institutional resilience encompassing economic factors (e.g., extent of property rights, extent of openness to trade and finance, and flexibility of exchange rates) and political ones (e.g., democracy, executive constraints, and the fiscal size of government). This index captures attributes that ought to be positively correlated with resilience, apart from size of government, which should be negatively correlated (a large government has little room to maneuver in the face of shocks). The graphs below illustrate our findings for economic and political resilience (the index ranges from 0 to 1) for selected country groups, although we have generated these indices for each of the over 90 individual countries in our data set (representing over 80% of global GDP). While our data go back to the 1960s, it is only by the 1990s that the widest array of variables considered are consistently available for countries beyond the advanced economies. As shown below, the 1990s and 2000s have seen a global rise in central bank resilience although there is considerable variation over time and the gaps between the country groups shown show fewer signs of convergence by the end of the sample that in the early 1990s. Gaps in political resilience remain throughout the sample considered and there is a marked drop for the G7 countries beginning in 2015 that predates the pandemic and recent events. The G7 were among the most politically resilient in the early 1990s.
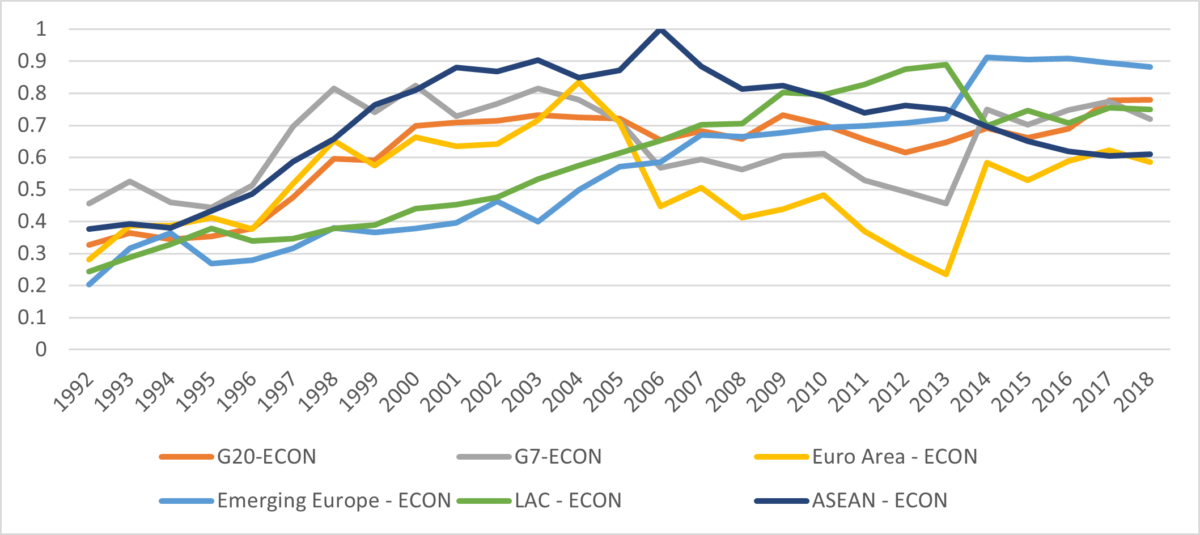
Figure 1: Economic Resilience. Higher scores imply greater resilience
Figure 2: Political Resilience. Higher scores imply greater resilience
We array this index against a measure of central bank effectiveness, which is linearly comprised of three separate components. First, we compare a central bank’s inflation performance against either stated goals – in the case of inflation targeting – or against an implicit goal (a five-year moving average of inflationary outcomes) – where banks have no pre-stated goal. Second, we fashion a measure of monetary policy uncertainty, measuring divergence of inflation and output outcomes versus forecasts. Finally, we measure how out of step a country’s inflation performance is with the world.
Using generalized method of moments (GMM), model selection techniques, and a local projection estimation from a VAR, we find that each percent decline in a central bank’s credibility corresponds with an average 3.6% drop in a country’s institutional resilience since the 1990s. Plainly put, the more that a central bank loses confidence via missing inflation targets or veering from global trends, the more harm it does to overall institutional resilience in a particular country.
The ramifications from this research once again highlight that central bank autonomy may lead to better inflation outcomes, but a central bank can still pursue poor policies or be ineffective even when independence is controlled for. A better performing central bank, that is, one that primarily focuses on price stability, is better for an economy; more importantly, with central banks playing such an important institutional role in an economy, a country’s overall institutional quality may also be dependent on how well a central bank performs. While our results rest on imperfect indicators we have attempted, within the constraints of data availability, to establish the sensitivity of our results to changes in definition, changes in sample periods, and sources of data. Our main findings remain substantially robust across estimation techniques employed.
This post written by Christopher Hartwell and Pierre Siklos.
Though the issue of the cause of cetral bank performance isn’t addressed directly, the authors seem to allow for the possibility that central banks can perform badly in controlling inflation because of factors outside their control. They do not, however, look into whether that difference matters.
Every central bank faced an inflationary shock due to Covid. Some responded badly – Turkey’s central bank, for instance. Some were faced with egregious policy errors from the government – the Bank of England comes to mind. Some were lucky in having an appreciating currency – the Fed, especially. Is there evidence that luck, good or bad, lead to changes in institutional resilience?
On another point:
“…a large government has little room to maneuver in the face of shocks.”
Is the U.S. federal government large, by the definition used by the authors? I ask because the U.S. government seems to me to have shown considerable flexibility un response to Covid and the Covid recession. In fact, the federal government also showed considerable flexibility in responding to the 2008-2009 financial crisis, though less in response to the mortgage and housing mess which helped precipitate the financial crisis.
Are we being treated to an ideological statement, or is there evidence to back up the assertion that big government is inflexible? I’d also ask if flexibility is the most important criterion in the face of shocks. A large government has numerous large existing channels through which to ameliorate shocks. Smaller governments have to create or expand such channels in order to use them. Does whatever inflexibility results from large size outweigh the benefits of large size in responding to shocks?
That is a pretty good point, I wonder if a federalist structure would have ameliorated some of the issues in a larger government, mainly because sub-national jurisdictions have their own fiscal pots to draw on. Our point was that larger governments, one that spend a lot already, have little fiscal room to maneuver in case of a shock.
“Never in the history of our Republic has a President had reason to believe that he would be immune from criminal prosecution if he used the trappings of his office to violate the criminal law,” wrote Sotomayor. “Moving forward, however, all former Presidents will be cloaked in such immunity. If the occupant of that office misuses official power for personal gain, the criminal law that the rest of us must abide will not provide a backstop. With fear for our democracy, I dissent,” Sotomayor concluded in her written opinion.
When she read her opinion the last line was
“With fear for our democracy, I and the Founding Father dissent”.
Now I hear the Chief Justice was upset with her dissent. Too bad – the Chief Justice basically put a torch to our Constitution. Worst majority opinion in the history of our nation.
Clarence Thomas wrote this Trump BS?
“No former President has faced criminal prosecution for his acts while in office in the more than 200 years since the founding of our country. And, that is so despite numerous past Presidents taking actions that many would argue constitute crimes. If this unprecedented prosecution is to proceed, it must be conducted by someone duly authorized to do so by the American people.”
GEE Clarence. What crimes did Washington commit? How about Lincoln? Or FDR? How about Saint Reagan? Funny Clarence cannot mention a single alleged crime committed by any other President besides maybe Nixon who had to be pardoned by Ford.
But dear Clarence had to bring up the civil case Clinton v. Jones. Which had nothing to do with this case at all. Except for the fact that Clarence is a Trumpian stooge who just so happened to sexually abuse Anita Hill.
Exactly. Everything has a first time. So the fact that it has not happened before is no argument that it should not happen now. The question is whether or not the constitution has protections for a President to commit crimes and not be held responsible for them because they were official acts. Nothing in the constitution has given the President such a right/protection – and if that is an error, it is not for the activist right wing SCOTUS to grab power to invent it. We have an orderly process for changing the constitution if the founding fathers missed out on something.
It has been suggested that the right wing SCOTUS judges have some kind of judicial philosophy that explains their decisions. This idea has been clearly debunked in the past few years. They have right wing political goals and they will apply or abandon whatever judicial principle or philosophy that can be used as an excuse for their decisions. They also have a lot of power and they know it – so they have become less and less concerned about trying to apply a fig leaf of judicial cover for their right wing political decisions and blatant corruption.