Addendum, A new paper by Chang Ma, John H. Rogers and Sili Zhou:
We provide perspective on the possible global economic and financial effects from COVID-19 by examining the handful of similar major health crises in the 21st century. We estimate the effects of these disease shock episodes on GDP growth, fiscal policy, expectations, financial markets, and corporate activity. Simple time-series models of GDP growth indicate that real GDP is 2.57 % lower on average across 210 countries in the year of the official declaration of the outbreak and is still 2.96 % below its pre-shock level five years later. The negative effect on GDP is felt less in countries with more aggressive first-year responses in government spending. Consensus forecast data suggests a pessimistic view on real GDP initially that lasts for two months, an effect that is larger for emerging market economies. Stock market responses indicate an immediate negative reaction. Finally, using firm-level data, we find a fall in corporate profitability and employment, and an increase in debt, the last of which is further reflected in higher sovereign CDS spreads.
Addendum, 4/1:
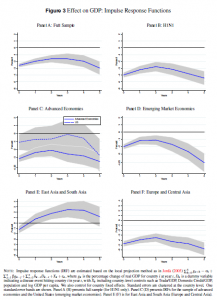
Impact on GDP growth expectations are illustrated in Figure 3:
One interesting (among many) policy relevant findings:
In countries with large responses of government expenditures, real GDP initially falls by 2.68% but the effect dies out in the second year. For the low government expenditure response countries, real GDP initially falls by 2.84%, an effect that is very persistent. Meanwhile, responses in government tax revenues do not make much of a difference.