From today’s FT:
Category Archives: financial markets
International Trade and Finance…and Policy
I’ve just returned from two highly stimulating conferences in Beijing. The first was a Columbia-Tsinghua conference on “Capital Flows and International Financial Systems”, organized by Jiandong Ju and Shang-Jin Wei, and the second a NBER-China Center for Economic Research conference on “China and the World Economy”, organized by Yang Yao, Shang-Jin Wei, and Chong-En Bai.
Negative interest rates
The European Central Bank announced on Thursday that it is moving interest rates into negative territory, charging banks for maintaining deposits with the ECB rather than paying the banks positive interest. The hope is that lower (now even negative) interest rates may provide some stimulus to the European economy which might help bring European inflation closer to the ECB’s 2% target. Here I offer a few thoughts on this move.
“Risk Aversion, Global Asset Prices, and Fed Tightening Signals”
In the IMF analysis of capital flows highlighted in yesterday’s post, the VIX is used to proxy for risk. This variable has a lot of explanatory power [1] [2], but there is more to be investigated. Jan Groen and Richard Peck at the NY Fed examine the nature of risk in international financial markets, in a Risk Aversion, Global Asset Prices, and Fed Tightening Signals :
The global sell-off last May of emerging market equities and currencies of countries with high interest rates (“carry-trade” currencies) has been attributed to changes in the outlook for U.S. monetary policy, since the sell-off took place immediately following Chairman Bernanke’s May 22 comments concerning the future of the Fed’s asset purchase programs. In this post, we look back at global asset market developments over the past summer, and measure how changes in global risk aversion affected the values of carry-trade currencies and emerging market equities between May and September of last year. We find that the initial signal of a possible change in U.S. monetary policy coincided with an increase in global risk aversion, which put downward pressure on global asset prices.
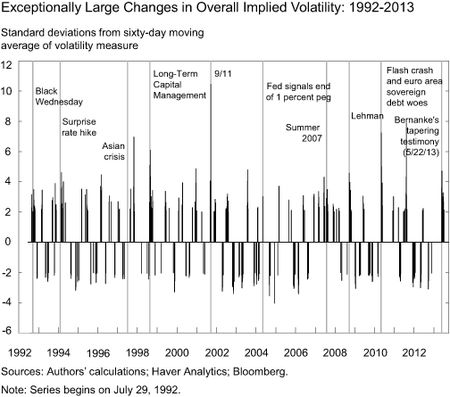
Implied volatility measures across different assets reflect, among other factors, market participants’ views on risk. Therefore, we conjecture that shifts in their risk aversion coincide with exceptionally large changes in implied volatility measures. An “exceptionally large” change in this case is defined as when overall implied volatility is at least two standard deviations above or below its mean over the previous sixty days. (“Overall implied volatility” is constructed as the average of the VIX index for U.S. equities, the Merrill Lynch Option Volatility Estimate [MOVE] Index for U.S. Treasury bonds, and the J.P. Morgan Global FX Volatility Index.) The chart below depicts changes in overall implied volatility for daily data from 1992 to September 2013, with labels for some key events that caused market turmoil. Exceptional volatility changes often occur in conjunction with these events, suggesting that these volatility changes are positively correlated with changes in (unobserved) risk aversion.
After examining the impact on the US dollar, carry trade returns and emerging market equity indices, the authors conclude:
Measuring changes to global risk aversion is a difficult exercise. The model used here suggests that substantial changes in risk aversion coincided with Chairman Bernanke’s May 22 testimony, resulting in substantial downward pressure on global asset prices in the two months after the May 22 testimony.
More in the post.
“Taper Tantrum or Tedium”
“How Will the Normalization of U.S. Monetary Policy Affect Latin America and the Caribbean?”
“Financial Adjustment in the Aftermath of the Global Crisis 2008-09: A New Global Order?”
That’s the title of a conference that took place at USC this weekend, co-organized by Joshua Aizenman, Menzie Chinn and Robert Dekle, and cosponsored by the USC Center for International Studies, USC School of International Relations, Journal of International Money and Finance, and the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco.
Addressing growing student debt
Mortgage and credit card debt today are lower than they were before the Great Recession. But the dollar value of outstanding student loans has surged, growing from 4% of GDP in 2007 to over 7% today.
The Ruble under Stress
Updated 3/4 5PM
Here are some immediate consequences of Russia’s intervention in the Ukraine. From Reuters:
Fed Policy and Emerging Market Economy Vulnerabilities
The recent weakness in emerging market currencies, and implementation of the taper, are sure to be topics of discussion at the G-20 meetings in Australia. While the imminent retrenchment in quantitative/credit easing is responsible for some of the currency movements of late, I’m not sure this is the only way to look at recent events; nor do I think we need see a replay of previous episodes of currency crises in response to US monetary tightening.
Digital transaction security
Bits and bytes can be stolen just like the cash under your mattress.