Down, down, down.
Category Archives: Trade Policy
Wisconsin in the Trade War of 2018-
I’m interviewed on Wisconsin Public Radio today, in the wake of declining Wisconsin exports.
The Relative Price of Soybeans vs. Grains, 2014-2019
Reader Ed Hanson insists I plot soybean prices from 2014 onward, instead of 2016, to show how factors other than tariffs affect soybean prices. I am happy to accommodate his request. I wonder why soybean prices suddenly deviate from grains overall, starting in March 2018.
Have All Agricultural Commodity Prices Behaved As Did Soybean Prices?
That’s what reader sammy asserts, trying to support the proposition that Chinese retaliatory tariffs on imports of US soybeans had no impact on US soybean prices.
… chart of soybean prices there are a number of other commodity price charts, such as copper, wheat, coffee etc. They are unaffected by the tariff war yet are remarkably similar to the soybean chart.
What a Trump Trade Victory Looks Like: Soybeans
Back in July 2018, reader CoRev wrote:
…no one has denied the impact of tariffs on FUTURES prices. Those of us arguing against the constant anti-tariff, anti-Trump dialogs have noted this will probably be a price blip lasting until US/Chinese negotiations end. We are on record saying the prices will be back approaching last year’s harvest season prices.
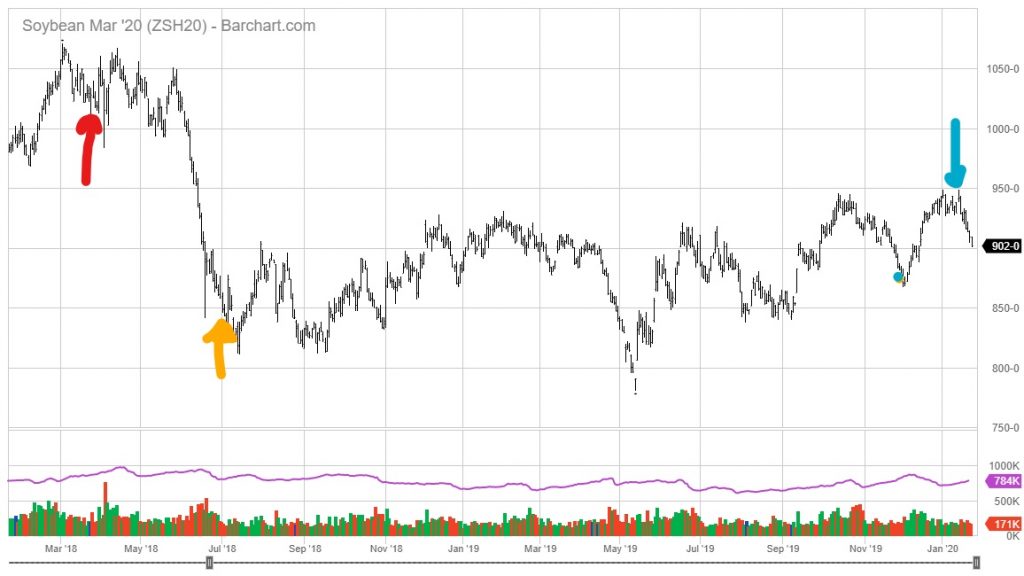
Back on March 23rd, when Mr. Trump announced intent to launch Section 301 actions, nearest month soybean futures closed at 1028. Latest today is 902. Indeed, prices have been falling since Mr. Trump signed the much heralded (by some) Phase 1 deal. This is shown in Figure 1 below.
Figure 1: Front month soybean futures (black). Trump announces intent of Section 301 action against China (red), Section 301 tariffs and Chinese retaliation in effect (orange arrow), and Phase 1 deal signed (blue arrow). Source: barchart.com.
Front month futures prices are now 14% lower now, while the CPI is 2.2% higher (both in log terms). You can do the math. The “blip” is not over.
The US China Phase 1 Deal Interpreted: Break Thing, Claim to Fix Thing, Repeat
Through 2018M03, US exports to China were growing smartly. The Section 232 and Section 301 actions were announced. The “deal” essentially restores real exports to China to the pre-shock trend for 2020, above for 2021 (if you believe!).
EconoFact: “What is the Toll of Trade Wars on U.S. Agriculture?”
By Menzie Chinn and Bill Plumley, at EconoFact, posted a few minutes ago:
U.S. agriculture has been caught in the tit-for-tat of the trade wars. Retaliation by China, Canada, Mexico, Turkey and members of the European Union to tariffs imposed by the Trump administration have taken a bite out of U.S. agricultural incomes. Tariffs on imports of steel and aluminum in the United States have also raised costs for machines, equipment and structures used by the agriculture sector. Agriculture incomes would have shown no growth in 2019 but for massive and unprecedented federal assistance. Even with this assistance, however, the agriculture sector shows signs of stress, with a rise in debt, a decrease in solvency and an increased number of bankruptcies.
The “Deal”: Much Ado About Nothing
Take a look at what exports to China will look like, with an additional $200 bn exports to China over two years, using the 2017 levels, as reported:
Navarro vs. Navarro
From WSJ today, an op-ed by Peter Navarro:
The national-security externalities associated with Trump trade policy may be even more consequential. A case in point is the tariffs being used as leverage to defend America’s technological crown jewels from being forcibly transferred to Chinese companies—from artificial intelligence, robotics and autonomous vehicles to quantum computing and blockchain. These industries comprise the core of the next generation of weapons systems needed to repel threats from rivals like China, Russia and Iran. One must ask the antitariff forecasters: Where are the benefits of a freer and more secure American homeland counted in your models?
From Peter Navarro, The Policy Game (Wiley, 1984), p.82, on the national security/trade policy nexus.
National Security Benefits and Costs. On the benefit side, protectionism within certain basic industries like autos, steel, and electronics helps to create and sustain and industrial base that, in times of war or national peril, can be shifted to defense purposes. However, this national security argument–and the existence of any benefits resulting from protecting these industries–can legitimately be called into question for several reasons.
First, the existence of any sizable benefits rests on the assumptions that import competition in our defense-related industries would not only reduce the size of these industries but also shrink them to the point where they would be too small to support our defense needs…
Second, it is highly possible that our defense capability might actually be enhanced–not damaged-by import competition. Without the umbrella of protectionism, our defense-related industries would be forced to operate at lowest cost, engage in more research and development, aggressively innovate to stay one step ahead of the competition, and modernize their plants at a faster pace. …
On the national security cost side, the major effect of protectionism is to threaten the stability of the international economic order through a global trade war. …
Full disclosure: I worked as a research assistant on this book.
Update, 1/15:
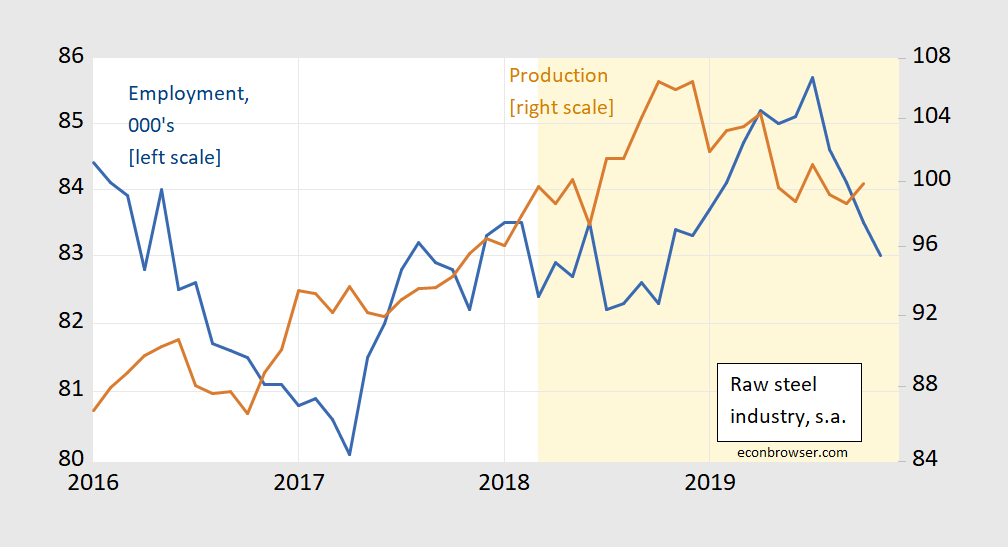
A picture of steel production and employment; Section 232 period shaded orange.
Figure 1: Employment in raw steel production (blue, left log scale), and industrial production (brown, right log scale). Light orange shading denotes Section 232 announcement and thereafter. Source: BLS, and Federal Reserve Board via FRED.
Dispatches from the Trade Wars
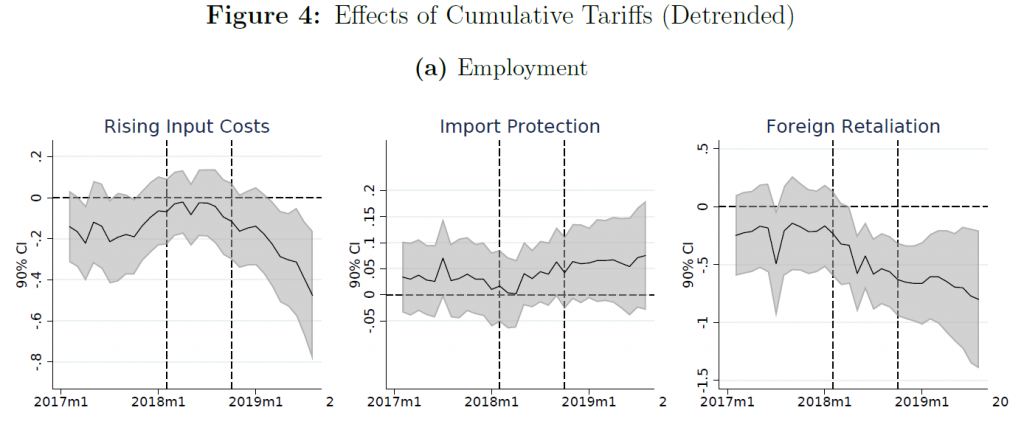
Net impact on employment from Trump’s trade war and associated retaliation:
Source: Flaaen and Pierce, 2019.